uitsluitend voor onderzoeksdoeleinden
Ganetespib (STA-9090) HSP90-remmer
Cat.Nr.S1159
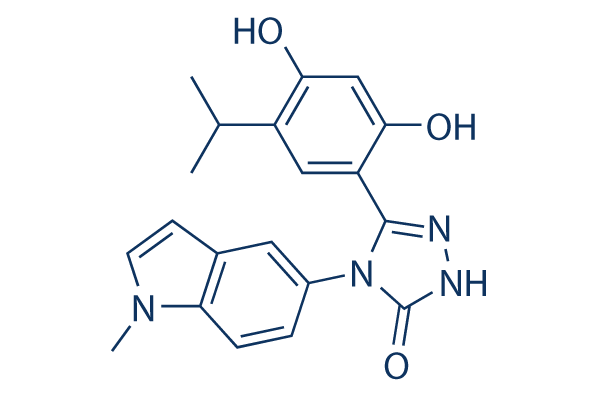
Chemische structuur
Moleculair gewicht: 364.4
Kwaliteitscontrole
| Gerelateerde doelwitten | Akt Wnt/beta-catenin PKC ROCK Microtubule Associated Integrin Bcr-Abl Actin FAK Kinesin |
|---|---|
| Overige HSP Inhibitoren | Tanespimycin (17-AAG) Elesclomol (STA-4783) Luminespib (NVP-AUY922) Alvespimycin (17-DMAG) Hydrochloride VER-155008 Onalespib (AT13387) BIIB021 Zelavespib (PU-H71) HSP990 (NVP-HSP990) NVP-BEP800 |
Celkweek, behandeling & werkconcentratie
| Cellijnen | Assaytype | Concentratie | Incubatietijd | Formulering | Activiteitsbeschrijving | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCI-H1975 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 72 h | IC50=8 nM | 22144665 | ||
| NCI-H1975 | Growth Inhibition Assay | 48 h | IC50=16 nM | 22144665 | ||
| Calu-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=64 nM | 23012248 | |||
| Calu-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=58 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H2122 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=53 nM | 23012248 | |||
| A549 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=43 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H358 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=29 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H1734 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H727 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28 nM | 23012248 | |||
| COR-L23 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H1792 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H2009 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=19 nM | 23012248 | |||
| SK-LU-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H2212 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H441 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H2030 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H23 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11 nM | 23012248 | |||
| HOP-62 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11 nM | 23012248 | |||
| IA-LM | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H460 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H157 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7 nM | 23012248 | |||
| H1355 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5 nM | 23012248 | |||
| VCaP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7 nM | 23152004 | |||
| LNCaP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 23152004 | |||
| Ramos-RA1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Karpas-299 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9.6 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Kasumi-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.8 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CCRF-CEM (2) | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.2 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CCRF-CEM (1) | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.5 nM | 23303741 | |||
| MOLT-4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.6 nM | 23303741 | |||
| RS4;11 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13.5 nM | 23303741 | |||
| COG-LL-317 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| NALM-6 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=11.7 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-136 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=23.2 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-90 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22.3 nM | 23303741 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=16.8 nM | 23303741 | |||
| NB-1643 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.9 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-258 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-10 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.7 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-9 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.6 nM | 23303741 | |||
| TC-71 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4.5 nM | 23303741 | |||
| CHLA-266 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27.1 nM | 23303741 | |||
| BT-12 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.3 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Rh30 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5.6 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Rh18 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6.2 nM | 23303741 | |||
| Rh41 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10.4 nM | 23303741 | |||
| RD | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 23303741 | |||
| K033 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| M23 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| K029 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| K028 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| K008 | Apoptosis Assay | 100 nM | 72 h | significantly induces apoptosis | 23418523 | |
| K033 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces a modest increase in G1 population | 23418523 | |
| M23 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces G1 and G2/M arrest | 23418523 | |
| K029 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces G1 arrest | 23418523 | |
| K028 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces G2 arrest | 23418523 | |
| K008 | Function Assay | 250 nM | 24 h | induces G2 arrest | 23418523 | |
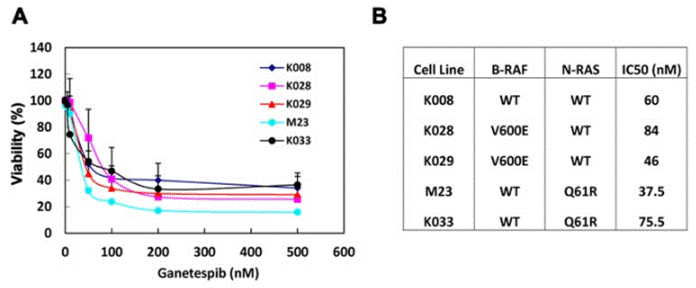
| K033 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=75.5 nM | 23418523 | |||
| M23 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=37.5 nM | 23418523 | |||
| K029 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=46 nM | 23418523 | |||
| K028 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=84 nM | 23418523 | |||
| K008 | Cell Viability Assay | IC50=60 nM | 23418523 | |||
| H3122 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | IC50=10 nM | 23533265 | |
| H2228 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | IC50=13 nM | 23533265 | |
| A1847 | Apoptosis Assay | 10-100 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces apoptosis time and dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| OVCAR-8 | Apoptosis Assay | 10-100 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces apoptosis time and dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| OVCAR-5 | Apoptosis Assay | 10-100 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces apoptosis time and dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| SKOV-3 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| A1847 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| OVCAR-8 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| OVCAR-5 | Cell Viability Assay | 0-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 23900136 | |
| H146 | Function Assay | 30 nM | 72 h | induces persistent G2/M phase arrest | 24166505 | |
| GLC4 | Function Assay | 30 nM | 72 h | induces persistent G2/M phase arrest | 24166505 | |
| H82 | Function Assay | 30 nM | 72 h | induces persistent G2/M phase arrest | 24166505 | |
| AC3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=25.9 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H1173 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=12.62 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H792 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45.07 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H620 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=32.67 nM | 24166505 | |||
| N592 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14.12 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H526 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21.64 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H187 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=24.99 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H146 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=28.51 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H128 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=69.55 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H69 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=83.36 nM | 24166505 | |||
| GLC4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=20.47 nM | 24166505 | |||
| H82 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=30.27 nM | 24166505 | |||
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 100 nM | 24 h | inhibits the migratory and invasive capacity | 24173541 | |
| BT-20 | Function Assay | 100/250 nM | 24 h | resulted in a dose-dependent destabilization of EGFR, IGF-IR, MET, and CRAF | 24173541 | |
| MDA-MB-435 | Function Assay | 100 nM | 30 min | inhibits accumulation of HIF-1α | 24248265 | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Function Assay | 100 nM | 30 min | inhibits accumulation of HIF-1α | 24248265 | |
| HCC2998 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=128 nM | 24682747 | |||
| SK-CO-1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=81 nM | 24682747 | |||
| LS-123 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=73 nM | 24682747 | |||
| SNU-C2B | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=45 nM | 24682747 | |||
| LS-1034 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=31 nM | 24682747 | |||
| LoVo | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=22 nM | 24682747 | |||
| COLO-678 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21 nM | 24682747 | |||
| NCI-H747 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17 nM | 24682747 | |||
| COLO-205 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14 nM | 24682747 | |||
| HCT 116 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=14 nM | 24682747 | |||
| HuTu-80 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=13 nM | 24682747 | |||
| HCT-15 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 24682747 | |||
| SW620 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=8 nM | 24682747 | |||
| LS-411 N | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=5 nM | 24682747 | |||
| RKO | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=4 nM | 24682747 | |||
| SW780 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=3451 nM | 24784839 | |||
| RT4 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=1733 nM | 24784839 | |||
| TCCSUP | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=142 nM | 24784839 | |||
| MGH-U3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=53 nM | 24784839 | |||
| HT-1197 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=53 nM | 24784839 | |||
| 5637 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=44 nM | 24784839 | |||
| 35612 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=38 nM | 24784839 | |||
| KU-19-19 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=36 nM | 24784839 | |||
| LB831-BLC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=34 nM | 24784839 | |||
| UM-UC3 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=33 nM | 24784839 | |||
| 647-V | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=27 nM | 24784839 | |||
| HT-1376 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=21 nM | 24784839 | |||
| J82 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=18 nM | 24784839 | |||
| BFTC | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=17 nM | 24784839 | |||
| SCaBER | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10 nM | 24784839 | |||
| 639-V | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=10 nM | 24784839 | |||
| RT112 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=9 nM | 24784839 | |||
| T24 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=7 nM | 24784839 | |||
| SW-1710 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6 nM | 24784839 | |||
| DSH1 | Growth Inhibition Assay | IC50=6 nM | 24784839 | |||
| CAL27 | Cytoxicity Assay | 10/50 nM | 24 h | decreases cell proliferation dose dependently | 25205430 | |
| Detroit562 | Cytoxicity Assay | 10/50 nM | 24 h | decreases cell proliferation dose dependently | 25205430 | |
| FUDA | Cytoxicity Assay | 10/50 nM | 24 h | decreases cell proliferation dose dependently | 25205430 | |
| SCC25 | Cytoxicity Assay | 10/50 nM | 24 h | decreases cell proliferation dose dependently | 25205430 | |
| HT-29 | Function Assay | 50nM | 24 h | DMSO | induced G0/G1 arrest | 25210794 |
| HCT-116 | Function Assay | 50nM | 24 h | DMSO | induced G0/G1 arrest | 25210794 |
| MGC-803 | Function Assay | 0.1-1000 nM | 24 h | induces G2/M cell-cycle arrest | 25590805 | |
| MKN-28 | Cell Viability Assay | 0.1-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 25590805 | |
| SGC-7901 | Cell Viability Assay | 0.1-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 25590805 | |
| MGC-803 | Cell Viability Assay | 0.1-1000 nM | 72 h | inhibits cell viability dose dependently | 25590805 | |
| MV411 | Apoptosis Assay | 30/80/150/250 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces dose dependant induction of apoptosis | 25882550 | |
| HL60 | Apoptosis Assay | 30/80/150/250 nM | 24/48/72 h | induces dose dependant induction of apoptosis | 25882550 | |
| TC32 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for TC32 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for A673 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Saos-2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Saos-2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| BT-37 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for BT-37 cells | 29435139 | |||
| RD | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for RD cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-SH | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-SH cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB1643 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB1643 cells | 29435139 | |||
| OHS-50 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for OHS-50 cells | 29435139 | |||
| A673 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Confirmatory screen for A673 cells) | 29435139 | |||
| SJ-GBM2 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SJ-GBM2 cells | 29435139 | |||
| SK-N-MC | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for SK-N-MC cells | 29435139 | |||
| NB-EBc1 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for NB-EBc1 cells | 29435139 | |||
| LAN-5 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for LAN-5 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Rh18 | qHTS assay | qHTS of pediatric cancer cell lines to identify multiple opportunities for drug repurposing: Primary screen for Rh18 cells | 29435139 | |||
| Klik om meer experimentele gegevens over de cellijn te bekijken | ||||||
Chemische informatie, Opslag en Stabiliteit
| Moleculair gewicht | 364.4 | Formule | C20H20N4O3 |
Opslag (Vanaf de ontvangstdatum) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS-nr. | 888216-25-9 | SDF downloaden | Opslag van stamoplossingen |
|
|
| Synoniemen | N/A | Smiles | CC(C)C1=C(C=C(C(=C1)C2=NNC(=O)N2C3=CC4=C(C=C3)N(C=C4)C)O)O | ||
Oplosbaarheid
|
In vitro |
DMSO
: 40 mg/mL
(109.76 mM)
Ethanol : 9 mg/mL Water : Insoluble |
Molariteitscalculator
|
In vivo |
|||||
In vivo Formuleringscalculator (Heldere oplossing)
Stap 1: Voer de onderstaande informatie in (Aanbevolen: Een extra dier voor het geval van verlies tijdens het experiment)
Stap 2: Voer de in vivo formulering in (Dit is alleen de calculator, geen formulering. Neem eerst contact met ons op als er geen in vivo formulering is in het gedeelte Oplosbaarheid.)
Berekeningsresultaten:
Werkconcentratie: mg/ml;
Methode voor het bereiden van DMSO-mastervloeistof: mg geneesmiddel vooraf opgelost in μL DMSO ( Concentratie mastervloeistof mg/mL, Neem eerst contact met ons op als de concentratie de DMSO-oplosbaarheid van de partij geneesmiddel overschrijdt. )
Methode voor het bereiden van in vivo formulering: Neem μL DMSO mastervloeistof, voeg vervolgens toeμL PEG300, mengen en helder maken, voeg vervolgens toeμL Tween 80, mengen en helder maken, voeg vervolgens toe μL ddH2O, mengen en helder maken.
Methode voor het bereiden van in vivo formulering: Neem μL DMSO mastervloeistof, voeg vervolgens toe μL Maïsolie, mengen en helder maken.
Opmerking: 1. Zorg ervoor dat de vloeistof helder is voordat u het volgende oplosmiddel toevoegt.
2. Zorg ervoor dat u het/de oplosmiddel(en) in de juiste volgorde toevoegt. U moet ervoor zorgen dat de verkregen oplossing, bij de vorige toevoeging, een heldere oplossing is voordat u verdergaat met het toevoegen van het volgende oplosmiddel. Fysische methoden zoals vortexen, echografie of een warmwaterbad kunnen worden gebruikt om het oplossen te bevorderen.
Werkingsmechanisme
| Targets/IC50/Ki |
HSP90
(OSA 8 cells) 4 nM
|
|---|---|
| In vitro |
De 50% remmende concentraties (IC50) voor Ganetespib (STA-9090) tegen maligne mestcellijnen zijn 10-50 keer lager dan die voor 17-AAG, wat aangeeft dat de triazolone-klasse van HSP90-remmers waarschijnlijk een grotere potentie vertoont dan geldanamycine-gebaseerde remmers. Deze verbinding remt MG63-cellijnen met een IC50 van 43 nM. Het bindt aan het ATP-bindende domein aan de N-terminus van Hsp90 en dient als een krachtige Hsp90-remmer door de afbraak te veroorzaken van meerdere oncogene Hsp90-cliëntproteïnen, waaronder HER2/neu, gemuteerd EGFR, Akt, c-Kit, IGF-1R, PDGFRα, Jak1, Jak2, STAT3, STAT5, HIF-1α, CDC2 en c-Met, evenals Wilms' tumor 1. Bij lage nanomolaire concentraties stopt het krachtig de celproliferatie en induceert het apoptose in een breed scala aan menselijke kankercellijnen, waaronder veel receptor tyrosinekinase-remmer- en tanespimycine-resistente cellijnen. Het vertoont krachtige cytotoxiciteit in een reeks solide en hematologische tumorcellijnen, inclusief die welke gemuteerde kinasen tot expressie brengen die resistentie verlenen tegen kleinmoleculaire tyrosinekinaseremmers. De behandeling veroorzaakte snel de afbraak van bekende Hsp90-cliëntproteïnen, vertoont een superieure potentie ten opzichte van de ansamycine-remmer 17-AAG, en toont aanhoudende activiteit, zelfs bij korte blootstellingstijden. In een andere studie induceert het apoptose van maligne canine mestcellijnen. Het is actief bij significant lagere concentraties voor C2 en BR canine maligne mestcellen met een IC50 van respectievelijk 19 en 4 nM, terwijl 17-AAG C2 en BR canine maligne mestcellen remt met een IC50 van respectievelijk 958 en 44 nM. Zowel de expressie van WT als mutant Kit wordt door 100 nM van deze verbinding na 24 uur in alle behandelde lijnen, inclusief C2- en BMCMCs-cellen, neerwaarts gereguleerd. Er worden echter geen effecten op PI3K- of HSP90-expressie waargenomen na behandeling ermee.
|
| In vivo |
Toediening van Ganetespib (STA-9090) leidt tot een significante tumorkrimp in verschillende tumorxenograftmodellen bij muizen en lijkt minder toxisch te zijn. Bovendien vertoonde deze verbinding een betere tumorpenetratie in vergelijking met tanespimycine. Het remt in vivo tumorgroei in zowel maligne mestcel- als OSA-xenograftmodellen. Ganetespib remt de tumorgroei significant wanneer het wordt toegediend in twee herhaalde cycli van 25 mg/kg/dag gedurende 3 dagen, met een %T/C-waarde van 18. Het wordt goed verdragen, waarbij de vehikel- en Ganetespib-groepen gemiddelde veranderingen in lichaamsgewicht vertonen ten opzichte van het begin van de studie van respectievelijk +0,3% en -8,1% op dag 17.
|
Referenties |
|
Toepassingen
| Methoden | Biomarkers | Afbeeldingen | PMID |
|---|---|---|---|
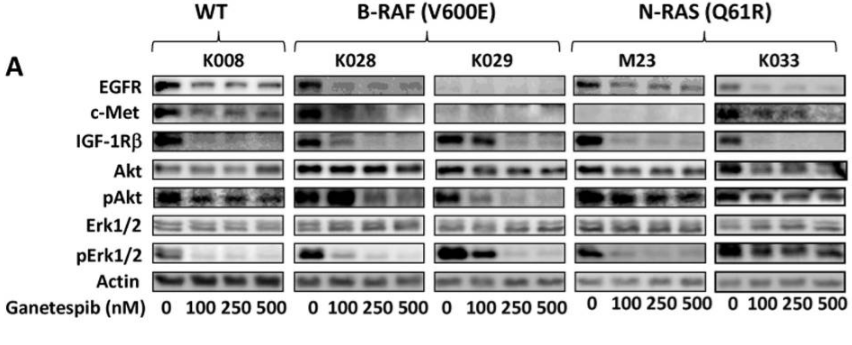
| Western blot | EGFR / c-Met / IGF-1Rβ/ Akt / p-Akt / ERK / p-ERK p27(Kip1) / p21 (Cip1) / Cyclin D1 / Cyclin E / Cyclin B1 / CDK1 / CDK2 / CDK4 Survivin / Bcl-2 / Bcl-xl / Mcl-1 B-RAF / C-RAF / N-RAS HER2 / p-STAT3 / BIM CDK1 / Cyclin D1 / Cyclin B1 / p27 c-PARP / c-caspase 3 / caspase 8 / c-caspase 8 / caspase 9 / c-caspase 9 ErbB2 / pErbB2 / Src / pSrc / mTOR / pmTOR / Bad / pBad / GSK3 / pGSK3 Wee1 / p-Wee1 / Chk1 / p-Chk1 |
|
23418523 |
| Growth inhibition assay | Cell viability |
|
23418523 |
Informatie klinische proef
(gegevens van https://clinicaltrials.gov, bijgewerkt op 2024-05-22)
| NCT-nummer | Rekrutering | Aandoeningen | Sponsor/Medewerkers | Startdatum | Fasen |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT02192541 | Terminated | Neoplasms |
National Cancer Institute (NCI)|National Institutes of Health Clinical Center (CC) |
December 2 2014 | Phase 1 |
| NCT02008877 | Completed | Malignant Peripheral Nerve Sheath Tumors (MPNST)|Sarcoma |
Sarcoma Alliance for Research through Collaboration|Synta Pharmaceuticals Corp.|United States Department of Defense |
December 2013 | Phase 1|Phase 2 |
Technische ondersteuning
Tel: +1-832-582-8158 Ext:3
Als u nog andere vragen heeft, kunt u een bericht achterlaten.
Veelgestelde vragen
Vraag 1:
Does this inhibitor inhibit both isoforms of HSP90?
Antwoord:
We don't have the information now and it is not very clear in the literature either. From following two references, it indicates that it might be specific to the alpha form “It binds to the ATP binding site of Hsp90 alpha with a Kd of 110 nM” http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3477583/
